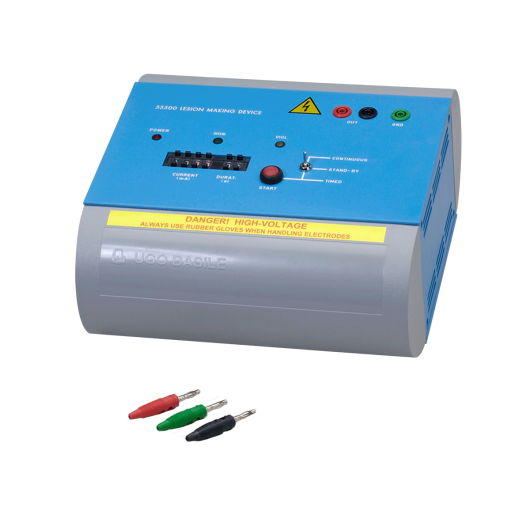
Lesion making device, LMD
Compact, direct current (DC) Lesion Maker for localized electrolytic lesions in the brain.
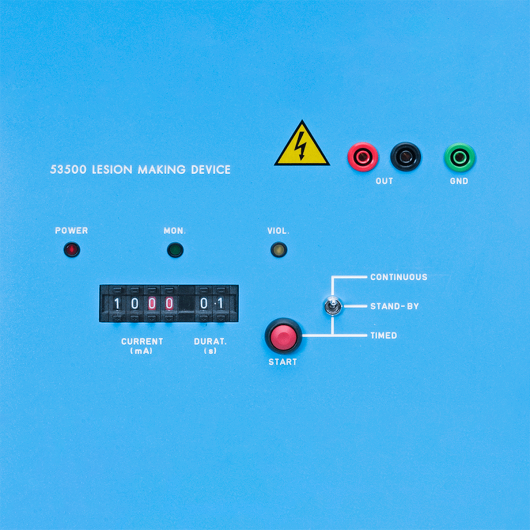
Isolated, regulated DC output for electrical safety. Two operating modes: Continuous and Timed.
Safe, localized, versatile
- Produces localized electrolytic lesions in small animals where DC (Direct Current) is preferred to RF (Radio Frequency).
- Regulated power supply with three operating modes: Continuous, Stand-by and Timed.
- Pre-set pattern can be selected by the operator.
- Versatile usage. Wide current output range (10uA-99mA) and duration (1-99 s) allows for virtually any procedure.
- Isolated output minimizes spurious current field lines across the tissue ensuring safety during operation.
- Violation LED indicator indicates if compliance is violated.
Features&benefits of making lesion device for rats or mice
- Current generator protected against short circuit: prevents damage to electronics, guarantees safety
- Wide current output range (10uA-99mA) and duration (1-99s): allows for virtually any procedure
- Three Operating Modes: Continuous, Stand-by and Timed
- Violation LED indicator: indicates if compliance is violated
Application of electrically induced lesion in mouse or rat
The surgically or electrically induced lesion has served as an important tool in the experimental search for function in the CNS. Its value has derived in part from the simplicity with which it can be used to study neural mechanisms of behaviour at a basic level. The advent of the stereotaxic technique, moreover, allowed researchers to produce discretely placed lesions with consistency, especially in subcortical structures of the brain.
The strength of the lesion technique resides also in the variety of ways with which to apply it. Manipulating the type of lesion (DC, RF, knife cut, etc.), its size, the type of electrode, the angle of entry, and so on, should continue to expose critically important aspects of neural functions because of the different effects that are produced.
It is no coincidence that the history of the development of these techniques is closely tied to the recent history of theories regarding localization of function in the brain. The traditional view, whose basic tenets are that (1) the functions are represented in discrete brain structures and that (2) the lesions disrupt function by removal of functional tissue in circumscribed sites, have been recently challenged by growing evidence of the importance of secondary changes. These are induced by a lesion, both directly (necrosis, anterograde and retrograde degeneration) and indirectly (transneuronal degeneration, regeneration and sprouting, alteration of neurochemical pools, vascular disruption) and may comprise the more significal neurological changes which can account for alteration of behaviour in a lesion experiment.
New strategy of research utilizing lesions is proposed, suggesting that greater emphasis be placed on the a posteriori assessment of secondary changes in the brain as they are correlated with changes in behaviour.
- 53500 Lesion making device
- 53500-310 Set of 3 output plugs
- E-AU 041 USB pen drive, including: 53500-302 Instruction manual
- 53500-325 Set of 2 stainless steel microelectrodes, custom FHC for Lesion Making Device, complete with black and red banana plug, and 1 meter cable
- UE(KK1) Stainless steel microelectrode, custom FHC (no wires)